Shark Zone: Why Baby Great Whites Are More Friend Than Foe Along California Coastlines
Science
2025-03-14 10:00:12Content
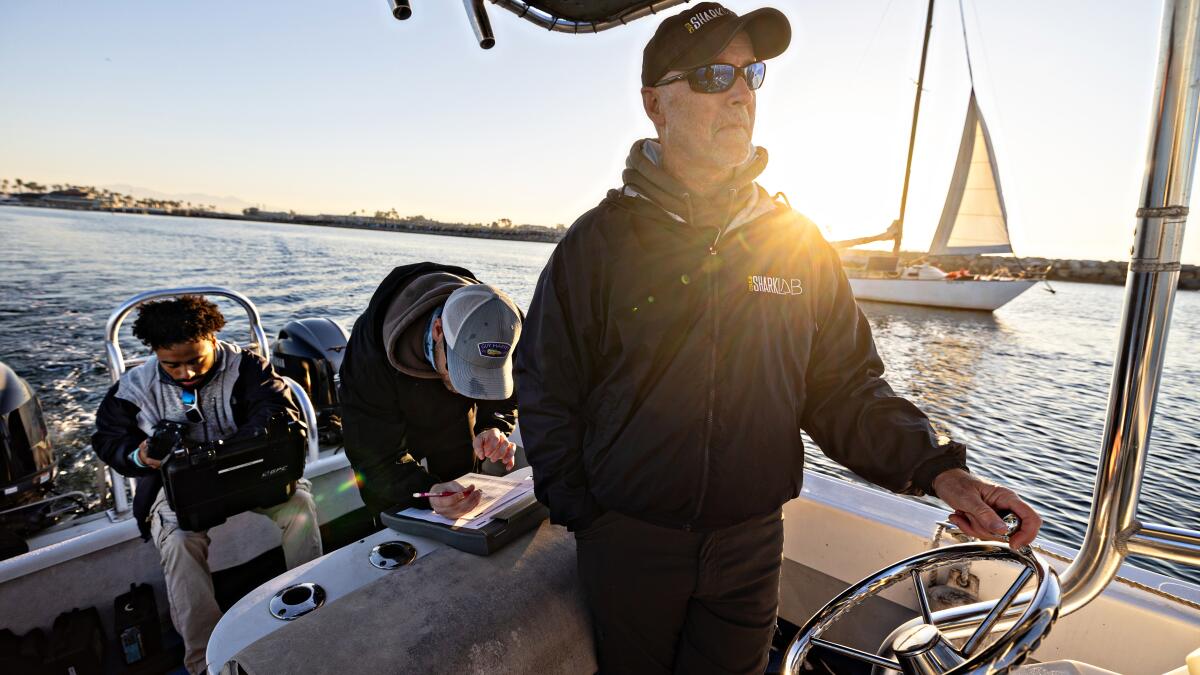

In a groundbreaking revelation, marine researchers at a prominent shark research laboratory have unveiled compelling evidence that challenges common perceptions about great white sharks. Their extensive tracking data suggests that juvenile great white sharks, some measuring an impressive nine feet in length, frequently navigate the waters near Southern California beaches, coexisting remarkably close to swimmers and surfers without displaying any predatory behavior.
The research team's comprehensive monitoring has uncovered a fascinating pattern of shark movement, revealing that these young marine predators seem surprisingly indifferent to human activity. Despite their formidable size and reputation, these juvenile sharks appear to be peacefully traversing coastal waters, demonstrating a level of proximity that might startle the average beachgoer.
This scientific observation provides a nuanced perspective on shark behavior, potentially reshaping public understanding of these often-misunderstood marine creatures. The data challenges sensationalized narratives about shark aggression and suggests a more complex, less threatening reality of shark-human interactions in coastal ecosystems.
Silent Sentinels: The Unexpected Coexistence of Great White Sharks and California Coastlines
In the vast, undulating waters off Southern California's picturesque coastline, a remarkable ecological narrative unfolds—one where massive predators navigate human recreational spaces with an almost imperceptible presence, challenging long-held perceptions about marine interactions and shark behavior.Unveiling the Hidden Marine Ecosystem: Where Sharks Swim Unnoticed
The Invisible Proximity: Shark Movements in Human Territories
Marine researchers have uncovered a fascinating phenomenon that fundamentally reshapes our understanding of shark-human interactions. Extensive tracking studies reveal that juvenile great white sharks, measuring up to nine feet in length, routinely traverse coastal waters frequented by swimmers and surfers, displaying a remarkable indifference to human presence. These marine predators, often portrayed as aggressive and threatening, demonstrate a nuanced behavioral pattern that contradicts popular media narratives. Their movements suggest a sophisticated navigational strategy that prioritizes environmental exploration over confrontational interactions.Scientific Insights: Decoding Shark Behavior Through Advanced Tracking
Cutting-edge tracking technologies have revolutionized marine biological research, providing unprecedented insights into shark migration patterns and behavioral dynamics. Sophisticated GPS and acoustic monitoring systems enable scientists to map intricate movement patterns with remarkable precision. Researchers employ advanced tagging methodologies that allow continuous monitoring of individual sharks, creating comprehensive databases that illuminate complex marine ecosystems. These technological innovations have transformed our comprehension of shark behavior from speculative assumptions to data-driven understanding.Ecological Significance: Sharks as Critical Marine Ecosystem Regulators
Great white sharks play a pivotal role in maintaining marine ecological balance. As apex predators, they regulate populations of various marine species, contributing to the intricate web of oceanic life. Their presence indicates robust marine health and demonstrates the delicate interconnectedness of coastal ecosystems. The seemingly casual navigation of these marine giants through human-populated waters underscores a critical environmental narrative—coexistence is not just possible but potentially harmonious when approached with scientific understanding and respect.Behavioral Patterns: Understanding Shark Indifference
Contrary to sensationalized portrayals, these juvenile great white sharks exhibit a remarkable level of environmental awareness that transcends predatory instincts. Their movement patterns suggest a complex cognitive process that prioritizes energy conservation and environmental exploration over potential confrontations. Researchers hypothesize that these sharks possess an intricate sensory system that allows them to distinguish between potential prey and non-threatening entities, enabling peaceful coexistence in shared marine spaces.Conservation Implications: Reframing Human-Shark Interactions
The emerging scientific narrative challenges traditional fear-based perspectives, advocating for a more nuanced approach to marine conservation. Understanding shark behavior through empirical research promotes responsible human interaction with marine environments. By recognizing these marine predators as integral components of complex ecological systems rather than threatening entities, we can develop more effective conservation strategies that protect both marine life and human recreational activities.RELATED NEWS
Science
Climate's Hidden Puzzle: How Local Signals Are Reshaping Our Understanding of Global Warming
2025-03-28 14:46:05
Science

Science Under Siege: How Anti-DEI Battles Are Eroding Research Diversity
2025-02-22 12:08:00
Science

Breaking: NIH Leadership Shakes Up Top Research Team in Unprecedented Purge
2025-04-01 22:15:00





