Factory Floor Fallout: U.S. Manufacturing Jobs Plummet to Lowest Point in Over a Decade
Manufacturing
2025-02-16 00:42:33Content

South Korea's manufacturing sector has experienced a significant downturn, with employment levels hitting a 12-year low in January, reflecting the country's ongoing economic challenges. According to recent data from Statistics Korea, the manufacturing workforce has shrunk to just 4.39 million workers, representing a substantial decline of 56,000 jobs compared to the same period last year.
This latest employment figure is particularly noteworthy as it matches levels not seen since January 2013, underscoring the persistent weakness in the country's industrial employment landscape. The decline highlights the mounting pressures facing South Korea's manufacturing industry, which has long been a cornerstone of the nation's economic strength.
The shrinking job market in this critical sector signals potential broader economic challenges, suggesting that businesses are struggling with reduced production demands and ongoing economic uncertainties. As companies adapt to changing market conditions, workers in the manufacturing sector continue to bear the brunt of these transformative economic shifts.
Manufacturing Sector in Crisis: South Korea's Economic Landscape Unravels
In the intricate tapestry of global economic dynamics, South Korea finds itself navigating treacherous waters as its manufacturing sector experiences unprecedented challenges, signaling potential systemic shifts in the nation's industrial ecosystem.Decoding the Silent Economic Tremors Reshaping Industrial Productivity
The Vanishing Manufacturing Workforce
The South Korean manufacturing landscape is undergoing a profound transformation, characterized by a dramatic decline in employment figures that paint a stark picture of economic uncertainty. Statistical evidence reveals a significant contraction, with employment numbers plummeting to levels not witnessed in over a decade. This downturn represents more than mere numerical fluctuations; it symbolizes a fundamental restructuring of industrial capabilities and workforce dynamics. Experts argue that this employment reduction stems from multiple interconnected factors, including technological disruption, global economic volatility, and shifting competitive landscapes. The manufacturing sector, traditionally a cornerstone of South Korea's economic prowess, now finds itself at a critical crossroads, grappling with unprecedented challenges that demand innovative strategic responses.Technological Disruption and Economic Recalibration
The current employment trends reflect a deeper narrative of technological metamorphosis. Automation, artificial intelligence, and advanced robotics are rapidly reshaping traditional manufacturing paradigms, rendering conventional workforce models increasingly obsolete. South Korean industries are experiencing a complex transition where human labor is being systematically replaced by sophisticated technological solutions. This technological revolution presents both unprecedented challenges and extraordinary opportunities. Companies must now navigate a delicate balance between maintaining human expertise and embracing cutting-edge technological innovations. The declining employment figures are not merely a statistical anomaly but a profound indicator of fundamental industrial restructuring.Global Economic Pressures and Competitive Dynamics
South Korea's manufacturing sector is simultaneously wrestling with intense global economic pressures. International trade tensions, supply chain disruptions, and evolving geopolitical landscapes contribute to an increasingly complex operational environment. The reduction in manufacturing jobs reflects a broader strategic recalibration as industries seek to optimize operational efficiency and maintain competitive edge. Multinational corporations and local enterprises are reevaluating their production strategies, often prioritizing technological integration and lean operational models. This strategic shift inevitably results in workforce reductions, presenting significant challenges for traditional employment structures and requiring comprehensive workforce adaptation strategies.Policy Implications and Future Trajectories
The current employment landscape demands immediate and strategic policy interventions. Government agencies and industrial stakeholders must collaborate to develop comprehensive reskilling programs, support technological education, and create adaptive economic frameworks that can absorb and transform potential workforce disruptions. Economic policymakers face the critical challenge of balancing technological progress with social stability. The manufacturing sector's transformation requires nuanced approaches that protect worker interests while simultaneously fostering innovation and maintaining international competitiveness.Socioeconomic Reverberations
Beyond numerical statistics, the declining manufacturing employment carries profound socioeconomic implications. Entire communities built around industrial ecosystems now confront potential economic reconfiguration. The ripple effects extend far beyond immediate job losses, potentially impacting education, urban development, and social mobility. Young professionals and emerging workforce generations must develop adaptive skills, embracing technological literacy and interdisciplinary capabilities to remain relevant in this rapidly evolving economic landscape. The traditional career trajectories are being fundamentally reimagined, necessitating unprecedented levels of personal and professional flexibility.RELATED NEWS
Manufacturing
Breaking: African Nations Forge Path to Vaccine Independence with Groundbreaking Manufacturing Deals
2025-02-14 19:11:07
Manufacturing
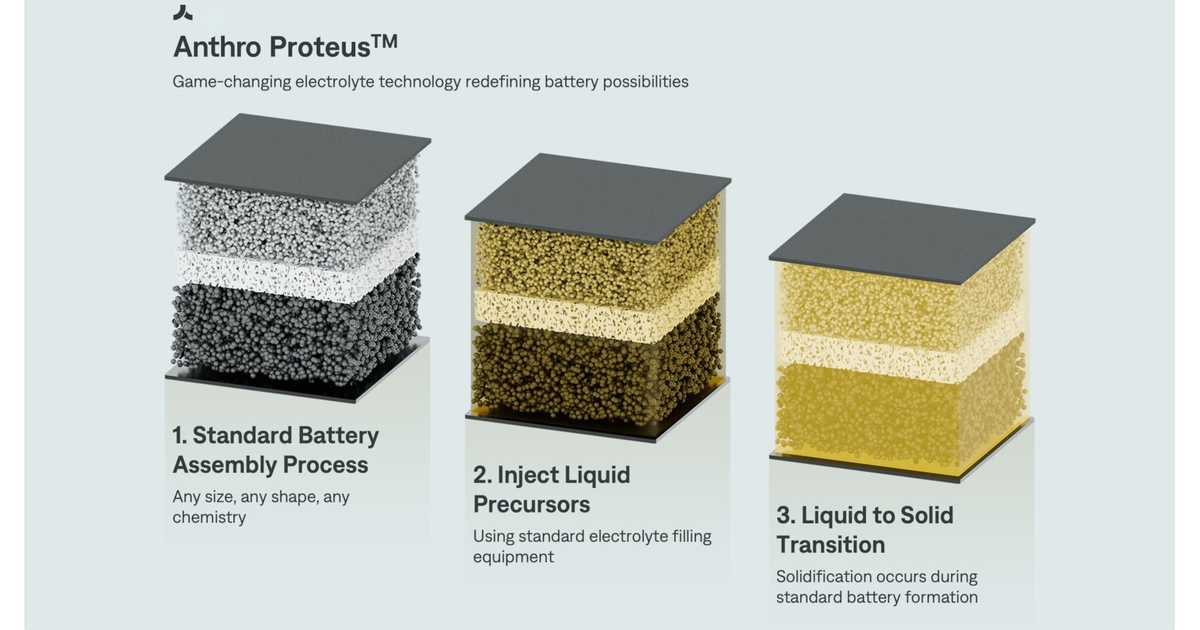
Revolutionary Battery Tech: Safer, Faster Charging Without Factory Overhaul
2025-02-25 21:11:50
Manufacturing

Powering American Industry: GE Aerospace Drops $1B Boost to Domestic Manufacturing
2025-03-13 13:50:41