When Life Almost Ended: The 5 Apocalyptic Moments That Reshaped Earth's History
Science
2025-03-28 13:00:00Content
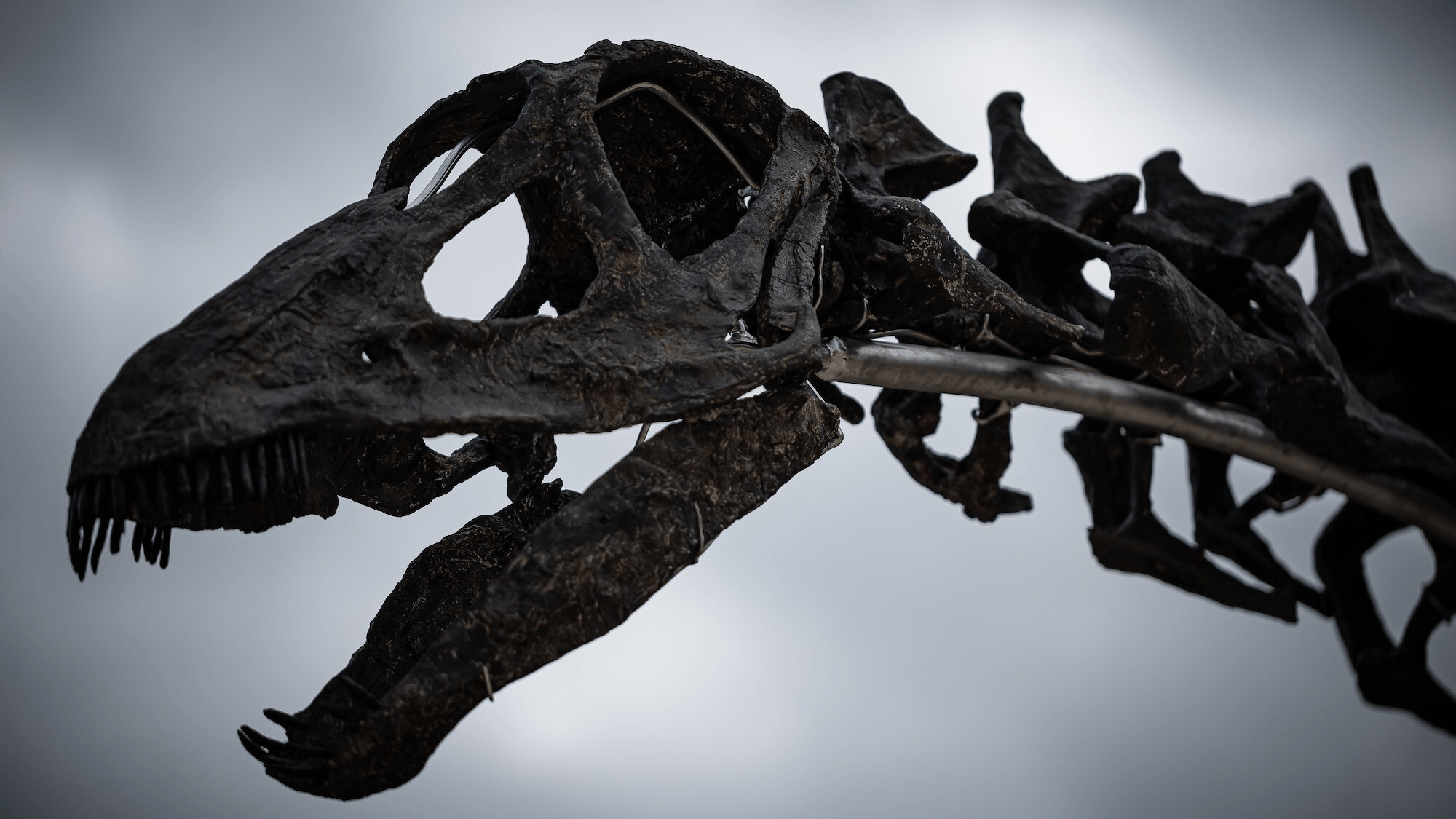
Throughout Earth's tumultuous 4.5-billion-year history, our planet has been a stage of constant transformation and devastating destruction. Powerful natural forces—volcanoes erupting with apocalyptic fury, massive asteroids crashing from the cosmos, and dramatic climate shifts—have repeatedly reshaped life's delicate tapestry, driving millions of species into extinction.
These planetary upheavals have not been mere isolated events, but rather a relentless cycle of creation and destruction. Volcanic eruptions have obliterated entire ecosystems, blanketing landscapes in ash and fundamentally altering environmental conditions. Massive asteroid impacts have triggered global catastrophes, causing widespread environmental collapse and triggering mass extinction events that reset the evolutionary clock.
Climate change, both gradual and sudden, has proven to be another formidable architect of biological destiny. Dramatic temperature fluctuations, shifts in sea levels, and radical transformations of habitats have challenged species' ability to adapt, ultimately leading to the permanent disappearance of countless life forms.
Each extinction event has been a stark reminder of nature's unforgiving complexity—a testament to the fragile balance of life on our dynamic, ever-changing planet. These historical transformations continue to fascinate scientists and serve as critical lessons in understanding the resilience and vulnerability of life itself.
Earth's Apocalyptic Symphony: How Planetary Forces Orchestrate Mass Extinctions
Throughout the vast tapestry of geological time, our planet has been a stage for relentless transformation, where cataclysmic events have repeatedly rewritten the narrative of life. From the primordial depths to the complex ecosystems we witness today, Earth has been an unforgiving crucible of survival, where species rise and fall in a perpetual dance of adaptation and annihilation.Unraveling the Mysteries of Planetary Destruction and Renewal
The Geological Architects of Extinction
Planetary destruction is not a singular event but a complex symphony of interconnected forces that reshape life's landscape. Volcanoes, those magnificent geological titans, have played a pivotal role in orchestrating mass extinctions throughout Earth's history. Their eruptions are not merely geological phenomena but transformative events that can fundamentally alter global ecosystems. Massive volcanic eruptions release unprecedented volumes of gases and particulate matter, creating atmospheric conditions that can trigger global climate shifts. The Siberian Traps eruption, for instance, is believed to have caused the most devastating mass extinction event in Earth's history, obliterating approximately 90% of marine species and 70% of terrestrial vertebrate species.Cosmic Interventions: The Asteroid Impact Paradigm
Beyond terrestrial mechanisms, extraterrestrial interventions have dramatically influenced life's trajectory. Asteroid impacts represent perhaps the most dramatic and instantaneous form of planetary transformation. The Chicxulub crater in Mexico, created by an asteroid approximately 10 kilometers in diameter, provides compelling evidence of how a single cosmic event can fundamentally alter global biodiversity. This monumental impact triggered immediate and long-lasting environmental changes. The collision generated massive tsunamis, triggered global wildfires, and launched enormous quantities of debris into the atmosphere, blocking sunlight and disrupting photosynthetic processes. The resulting climate collapse led to the extinction of dinosaurs and paved the way for mammalian dominance.Climate Change: The Slow-Motion Extinction Engine
Climate change represents a more gradual yet equally potent mechanism of species elimination. Unlike sudden catastrophic events, climate transformations create prolonged environmental stress that challenges species' adaptive capabilities. Historical climate shifts have demonstrated remarkable power in reshaping biological landscapes. During the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum, rapid global warming triggered massive ecological reorganizations. Ocean acidification, temperature fluctuations, and disrupted precipitation patterns forced numerous species to migrate, adapt, or face extinction. These events underscore the delicate balance between environmental conditions and biological survival.Evolutionary Resilience and Adaptation
Despite repeated planetary upheavals, life demonstrates extraordinary resilience. Each mass extinction event has paradoxically served as a catalyst for evolutionary innovation. The elimination of dominant species creates ecological niches that enable novel life forms to emerge and flourish. Mammals, for example, survived and eventually thrived following the dinosaur extinction, transitioning from marginal creatures to dominant terrestrial and marine organisms. This evolutionary narrative highlights nature's remarkable capacity for regeneration and adaptation in the face of seemingly insurmountable challenges.Contemporary Implications and Future Projections
Understanding historical extinction mechanisms provides critical insights into contemporary environmental challenges. Human-induced climate change mirrors many characteristics of previous planetary transformations, raising profound questions about biodiversity's future. Current scientific models suggest that anthropogenic activities are accelerating extinction rates at unprecedented speeds. The intricate interplay between human intervention and natural planetary processes creates a complex scenario with potentially far-reaching consequences for global ecosystems. By comprehending these historical patterns, we gain invaluable perspectives on our planet's dynamic nature and the fragile interconnectedness of life's intricate web.RELATED NEWS
Science

Space Explorers Reveal Secrets: Inside NASA and SpaceX's Latest Cosmic Expedition
2025-03-24 14:03:02
Science

Local Teen Shatters Scholarship Records: Prince William Student Wins $27K in Groundbreaking Science Challenge
2025-02-25 01:50:00