Forging the Future: Siemens and Michigan Unite to Revolutionize Metal 3D Printing Education
Manufacturing
2025-02-24 16:23:46Content

Exploring the Cutting-Edge World of Metal 3D Printing
Metal 3D printing has emerged as a revolutionary manufacturing technology that is transforming how industries design and produce complex metal components. This innovative process goes far beyond traditional manufacturing methods, offering unprecedented flexibility and precision in creating intricate metal parts.
Understanding the Metal 3D Printing Process
At its core, metal 3D printing involves layering metallic materials using advanced digital design techniques. The process begins with a detailed 3D computer model, which is then translated into thin layers that are precisely deposited and fused together. Various techniques like selective laser melting (SLM) and direct metal laser sintering (DMLS) enable manufacturers to create highly sophisticated metal objects with remarkable accuracy.
Key Advantages of Metal 3D Printing
- Unprecedented design complexity
- Significant weight reduction
- Rapid prototyping capabilities
- Minimal material waste
- Enhanced customization potential
Diverse Applications Across Industries
Metal 3D printing has found critical applications in aerospace, automotive, medical, and engineering sectors. From creating lightweight aircraft components to producing patient-specific medical implants, this technology is pushing the boundaries of what's possible in manufacturing.
Recognizing Technological Limitations
Despite its remarkable capabilities, metal 3D printing is not without challenges. High equipment costs, limited production speeds, and material constraints remain significant hurdles for widespread adoption. Ongoing research and technological advancements continue to address these limitations, promising an exciting future for this transformative technology.
Conclusion
Metal 3D printing represents a paradigm shift in manufacturing, offering unprecedented design freedom and innovation potential. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more groundbreaking applications and solutions across various industries.
Revolutionizing Manufacturing: The Cutting-Edge World of Metal 3D Printing Technology
In the rapidly evolving landscape of advanced manufacturing, metal 3D printing emerges as a transformative technology that is reshaping how industries conceptualize, design, and produce complex components. This groundbreaking approach to manufacturing represents a quantum leap beyond traditional fabrication methods, offering unprecedented precision, flexibility, and innovation across multiple sectors.Unlock the Future of Manufacturing: Where Imagination Meets Metallic Precision
The Technological Foundations of Metal 3D Printing
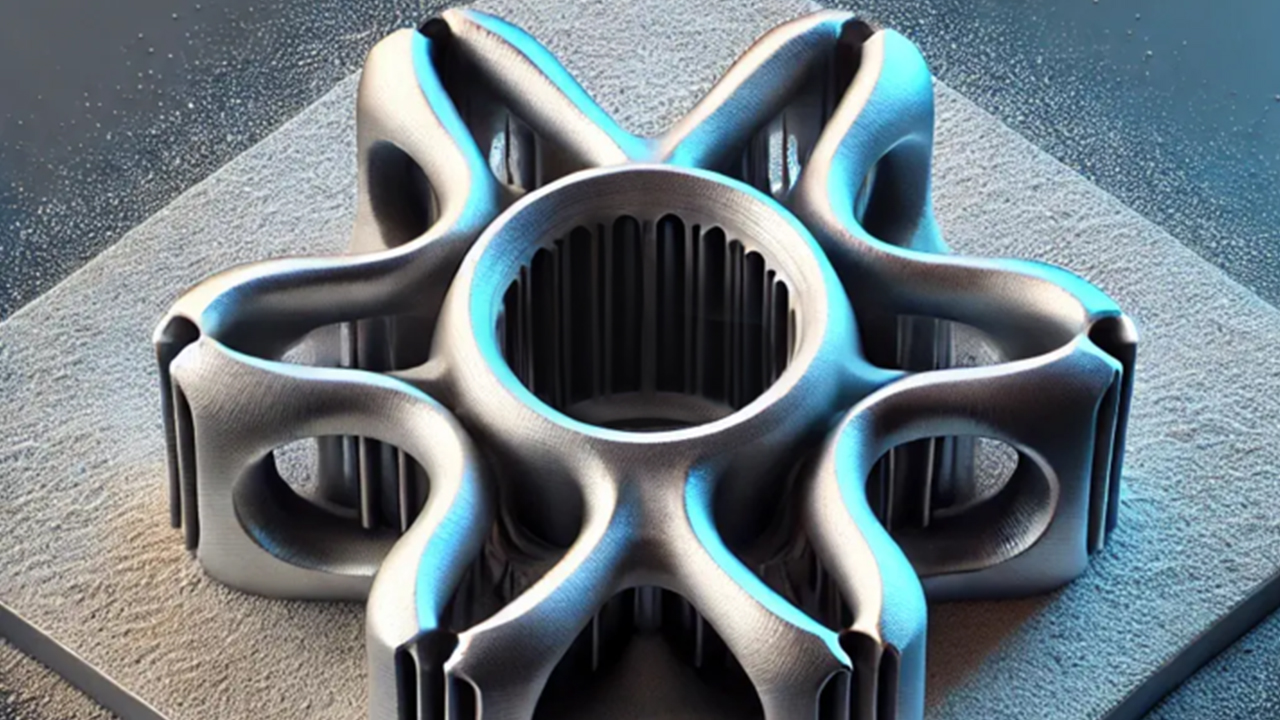
Metal 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, represents a paradigm shift in production methodologies. Unlike conventional subtractive manufacturing techniques that remove material to create components, this revolutionary process builds objects layer by layer using advanced metallic powders and sophisticated laser technologies. Engineers and designers can now transform intricate digital designs into tangible, high-performance metal objects with remarkable accuracy and complexity. The process begins with sophisticated computer-aided design (CAD) models that serve as digital blueprints. Powerful laser systems meticulously scan and fuse metallic powders, creating three-dimensional structures with microscopic precision. This technique allows for the creation of geometrically complex parts that would be impossible or prohibitively expensive using traditional manufacturing methods.Diverse Applications Across Industrial Landscapes
The potential applications of metal 3D printing span numerous critical industries. In aerospace, manufacturers can produce lightweight, intricate engine components that reduce overall vehicle weight and enhance fuel efficiency. Medical device companies leverage this technology to create patient-specific implants with unprecedented customization, while automotive manufacturers develop complex engine parts with optimized internal structures. Aerospace engineers, for instance, can now design turbine blades with internal cooling channels that were previously unimaginable. Medical researchers create personalized orthopedic implants that perfectly match a patient's unique anatomical requirements. Automotive designers prototype and produce complex engine components that dramatically improve performance and reduce manufacturing costs.Technological Processes and Methodological Innovations
Multiple metal 3D printing techniques have emerged, each with unique characteristics and advantages. Selective Laser Melting (SLM) represents one of the most sophisticated approaches, utilizing high-powered lasers to completely melt and fuse metallic powders. Electron Beam Melting (EBM) offers an alternative method, employing electron beams in vacuum environments to create highly dense metal components. These processes require extraordinary precision and control. Sophisticated software algorithms manage laser power, scanning strategies, and powder distribution, ensuring consistent material properties and structural integrity. Temperature control, powder quality, and laser parameters must be meticulously managed to produce components with optimal mechanical characteristics.Challenges and Technological Limitations
Despite its immense potential, metal 3D printing confronts several significant challenges. The current technology remains expensive, with high equipment and material costs limiting widespread adoption. Complex post-processing requirements, including heat treatment and surface finishing, add additional complexity and expense to the manufacturing process. Material limitations also present ongoing challenges. Not all metal alloys are equally suitable for 3D printing, and researchers continue developing new powder compositions and printing strategies to expand material compatibility. Surface roughness, internal porosity, and mechanical properties require continuous refinement to meet stringent industrial standards.Future Horizons and Emerging Innovations
The future of metal 3D printing looks extraordinarily promising. Emerging research focuses on developing faster printing technologies, expanding material options, and reducing overall production costs. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are being integrated to optimize printing parameters, predict potential defects, and enhance overall manufacturing efficiency. Interdisciplinary collaborations between materials scientists, software engineers, and manufacturing experts are driving unprecedented innovations. Universities and research institutions worldwide are investing significant resources into advancing metal 3D printing technologies, suggesting we are merely scratching the surface of this transformative manufacturing approach.RELATED NEWS

Titans of Industry: Goodyear's Top Performers Revolutionize Manufacturing Excellence
From Scrap to Salvation: How 3D Printing is Rescuing Military Vehicles on the Battlefield